The pigment melanin is responsible for the amazing range of human skin tones, eye hues, and hair colours. While melanin is often discussed, its biological advantages are seldom mentioned. Melanin has two important functions in the human body: it produces pigmentation for the skin, hair, and eyes, and it shields the body from the sun's damaging ultraviolet (UV) radiation. This article will explain what melanin is, why it's vital for the skin, and how several circumstances might affect your melanin levels.
What is Melanin?
Melanin is a complex pigment that gives humans our characteristic hair, skin, and eye colour. Pigmentation in the hair, skin, and eyes of humans and animals is caused by two forms of melanin, but melanin is typically considered a single pigment. Within the human brain lies the third form of melanin called neuromelanin, which provides pigment to the brain's structures. Neuromelanin is not responsible for facial pigmentation like eumelanin and pheomelanin.
However, the association between this melanin and Parkinson's disease has been the primary focus of research. Melanocytes are big cells that may be found throughout the body and are responsible for the first stages of melanin formation. Melanocytes produce pigment-forming melanosomes. These melanosomes are where eumelanin and pheomelanin are synthesized before being transferred to other cells like keratinocytes (skin cells).
Suggested Read: Hyperpigmentation: Causes And Treatment
Types of Melanin
Eumelanin, pheomelanin, and neuromelanin are the three types of melanin in humans.
1. Eumelanin
 Eumelanin
EumelaninA person's hair colour might be affected by their eumelanin levels. A higher concentration of the black or brown pigment eumelanin causes hair to be darker, whereas a lower quantity produces hair of a lighter shade.
Also Read: Use Vitamin C To Remove Hair Color
2. Pheomelanin
 Pheomelanin
PheomelaninChanges in pheomelanin levels cause the skin to appear pink, red, and yellow undertones. When pheomelanin and eumelanin are present in equal amounts, the outcome is red hair.
Relatable Read: Three Main Types of Skin Undertone
3. Neuromelanin
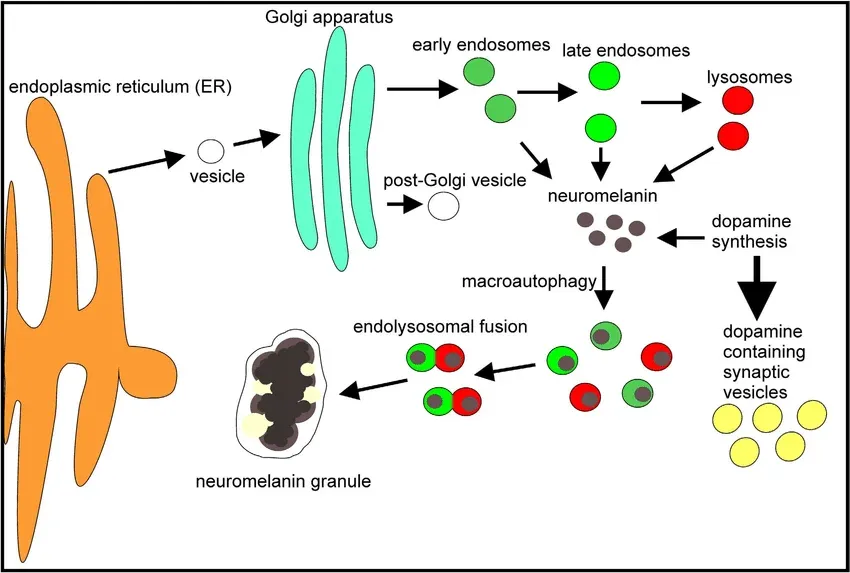 Neuromelanin
Neuromelanin Neuromelanin gives certain areas of the brain its characteristic dark hue. Evidence suggests that this pigment has a role in protecting brain cells from dying. Parkinson's disease is a neurologic illness that may be affected by a lack of neuromelanin.
Benefits of Melanin
It's well known that melanin is crucial in providing pigment to the skin, hair, and eyes. Additional benefits of melanin are a by-product of their use.
1. Shade from the Sun's Harmful Rays
Melanin can take in UV radiation and then disperse it throughout the body. It shields one's nucleus, where one's genetic information is stored, from harmful radiation. Pigmentation in the skin blocks ultraviolet light, which may cause cancer by destroying DNA.
2. Antidote against Harmful Reactive Oxygen Species
Melanin's protection against ROS is ensured by its antioxidant capabilities (ROS). These byproducts originate from the body's cellular functions. Accumulated reactive oxygen species (ROS) are harmful to cells. Diseases including cancer, diabetes, and aging have all been linked to ROS. When UV rays create oxidative stress on the skin, melanin may scavenge the reactive oxygen species (ROS) that are produced.
Other Benefits
Research conducted on animals has shown a number of other possible advantages associated with melanin. For instance, research conducted in 2016 on rats indicated that herbal melanin might be able to inhibit the onset of gastrointestinal ulcers. This lends credence to the idea that melanin may play a part in the defence mechanisms of the gut. In addition, earlier studies have shown that melanin may have a role in the decrease of inflammation throughout the body, therefore protecting the liver from being damaged. Additionally, it may have an effect on the body's immunological system.
Does Melanin affect Skin Colour?
Melanin is a naturally occurring pigment that gives your hair, eyes, and skins their colour. When your body produces more melanin, your hair, skin, and eyes will darken. Genetics and the quantity of sun exposure your ancestors had both play a role in determining how much melanin your body produces. The pigments eumelanin and pheomelanin work together to create your skin, hair, and eye colours. The number of melanocytes in the human body is mostly constant. However, these melanocytes generate varying levels of melanin. Those with higher melanin levels tend to have darker hair, eyes, and complexion than those with lower levels. Freckles are also a result of a predisposed cluster of melanocytes.
Factors Influencing the Amount of Melanin in the Skin
Melanin levels are largely determined by
- Genetics
- Sun Exposure
- Hormones &
- Age
The major contributor to melanin levels in the skin is the individual's genetic makeup.
How does Melanin respond when Exposed to Sunlight?
Melanin acts as a protection for the skin, preventing it from being damaged by the sun. It is the body's natural defence system against being sunburned. When sun rays strike the skin, the body creates a hormone that attaches to cells that make melanin. This causes the skin to darken. This causes them to produce extra melanin, which serves as an additional kind of defence.
The pigment melanin is initially located in the basal layer of the epidermis, and it gradually becomes more concentrated as it moves upward through the epidermis. Burns are caused by ultraviolet B radiation from the sun, which chars the epidermis, the topmost layer of skin. Tans are the result of exposure to UVA radiation. UVA rays are able to pass through the epidermis and reach the deeper layers of the skin. It is in this area that they promote the production of melanin by the melanocytes.
Melanin is the dark pigment that is responsible for tanning and also acts as a natural sunscreen when exposed to the sun. Melanin is a form of pigment that may be found in human and animal hair, skin, and eyes. It is responsible for the colouration of these body parts. In addition to providing colour for the cells, melanin also guards against damage to the cells that may be caused by exposure to UV radiation by absorbing the UV rays that are detrimental to the cells.
To a large extent, melanin levels are predetermined by a person's genes; nevertheless, these levels are susceptible to change from various environmental factors, including age, sun exposure, and hormones.
Read Next: Beat The Heat- Protect Your Hair And Skin
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is there a Connection between Melanin and Melatonin?
No. The words may seem the same, but they mean completely distinct things.
Q2. Does having Dark Skin prevent you from getting enough Vitamin D?
Lack of vitamin D is more common in those with darker skin tones. The skin's naturally high melanin content blocks most sun rays.
Q3. Can Dark Skin be attributed to Melanin?
The darkening of the skin is a real side effect of an overabundance of melanin.
Also Read: Get Rid Of Your Summer Tan

